|
※サムネイル画像をクリックすると拡大画像が表示されます。
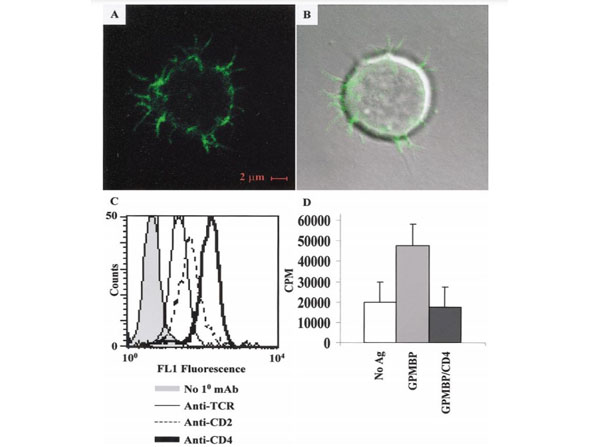
Donor R1-trans T-APC have I-A dendrites. R1-trans T-APC were labeled with OX6-FITC (mouse anti-rat I-A mAb). Cells were then examined via confocal microscopy and were viewed in a FITC channel (A) or an overlay of FITC and DIC channels (B). (C) R1-trans T-APC were stained with no primary mAb (shaded line), R73 (anti-TCR) (thin line), OX34 (anti-CD2) (dashed line), or W3/25 (anti-CD4) (boldface line) and a goat anti-mouse FITC-conjugated secondary. (D) R1-trans T-APC were cultured in the presence (gray bar) or in the absence (white bar) of 3.2 M GPMBP with (black bar) or without W3/25 (anti-CD4) for 2 days. GPMBP was purified from guinea pig spinal cords (p/n GP-T065). During the last 24 h of the culture, the cultures were pulsed with 1 μCi of [3 H]thymidine. T cells were harvested onto filters to measure [3 H]thymidine incorporation by scintillation counting.FIG. 2. PMID: 11902826.
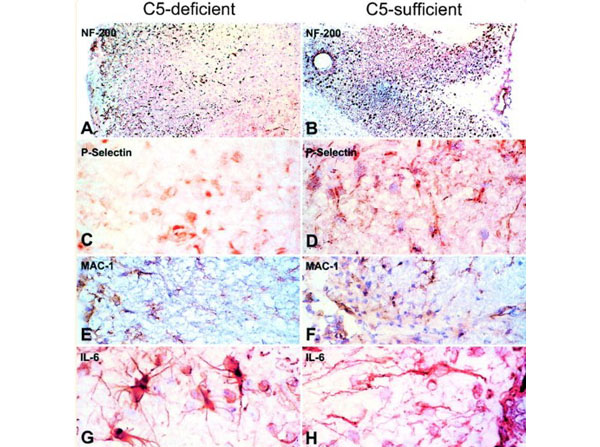
Immunohistochemistry of C5-d and C5-s mice with EAE. EAE was induced by subcutaneous injection of 700 μg purified guinea pig myelin from frozen spinal cords (p/n GP-T065), in incomplete Freund’s adjuvant containing 70 μg?Mycobacterium tuberculosis?and H37RA, followed by intravenous injection with 100 ng Pertussis toxin, on day 0, 2, and 7 post-immunization (p.i.). Neurofilament (NF-200): Sections from C5-d with chronic EAE revealed weaker and scattered staining of NF-200 (A) in areas corresponding to a chronic lesion, compared to the robust, densely-packed staining in sections of C5-s mice (B), where most axons survived. P-Selectin: In chronic EAE, staining for the endothelial adhesion molecule, P-Selectin, was lower in C5-d (C) than C5-s (D), perhaps indicating reduced infiltration of inflammatory cells into the tissue. MAC-1: Increased staining of macrophages in C5-s mice (E), during acute disease suggested enhanced phagocytosis of myelin debris in C5-s, in comparison to C5-d mice (F). IL-6: In acute EAE, IL-6 was enhanced in reactive astrocytes in C5-d (G), in comparison to C5-s mice (H). Magnifications:?A?and?B, ×63;?E,?F,?G,?H, ×625.Fig 4. PMID: 12937147.
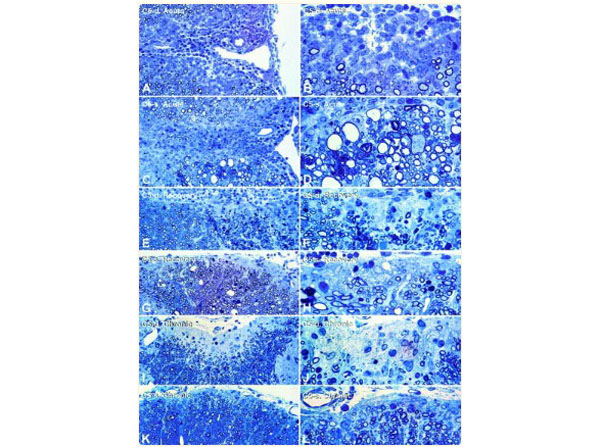
Histopathology of acute, recovery, and chronic phases of EAE in C5-d and C5-s mice. EAE was induced by subcutaneous injection of 700 μg purified guinea pig myelin from frozen spinal cords (p/n GP-T065), in incomplete Freund’s adjuvant containing 70 μg?Mycobacterium tuberculosis?and H37RA, followed by intravenous injection with 100 ng Pertussis toxin, on day 0, 2, and 7 post-immunization (p.i.). Toluidine-blue-stained epoxy sections (1 μm) from the upper lumbar of C5-d mice with acute EAE (A?and?B), revealed well-demarcated, confined lesions with inflammation and a narrow rim of demyelinated axons. Lesions of C5-s mice with acute EAE (C?and?D) are more diffuse and display inflammation and demyelination in addition to Wallerian degeneration (D,?lower left), dystrophic axons (D,?center right), and myelin ovoids (D,?left). In the recovery phase of EAE, C5-d mice (E?and?F, cervical spinal cord) show extensive Wallerian degeneration (dense droplets,?lower right) and demyelination. In contrast, extensive remyelination was present in C5-s mice (G?and?H, S1 spinal cord), shown by numerous thinly myelinated fibers along the meningeal surface (H). Numerous fibrous astrocytes with pale nuclei occur within the remyelinated zone. During chronic EAE, C5-d mice (I?and?J) developed a prominent zone of intense gliosis at the margin of the spinal cord, from which nerve fibers and oligodendrocytes were depleted. Lesions in C5-s mice (K?and?L) displayed numerous remyelinated axons at the edge of the spinal cord, where some gliosis is also present.Fig 3. PMID: 12937147.
|

|
|
Donor R1-trans T-APC have I-A dendrites. R1-trans T-APC were labeled with OX6-FITC (mouse anti-rat I-A mAb). Cells were then examined via confocal microscopy and were viewed in a FITC channel (A) or an overlay of FITC and DIC channels (B). (C) R1-trans T-APC were stained with no primary mAb (shaded line), R73 (anti-TCR) (thin line), OX34 (anti-CD2) (dashed line), or W3/25 (anti-CD4) (boldface line) and a goat anti-mouse FITC-conjugated secondary. (D) R1-trans T-APC were cultured in the presence (gray bar) or in the absence (white bar) of 3.2 M GPMBP with (black bar) or without W3/25 (anti-CD4) for 2 days. GPMBP was purified from guinea pig spinal cords (p/n GP-T065). During the last 24 h of the culture, the cultures were pulsed with 1 μCi of [3 H]thymidine. T cells were harvested onto filters to measure [3 H]thymidine incorporation by scintillation counting.FIG. 2. PMID: 11902826.
|
|
| 種由来 |
Guinea Pig
|
| 由来詳細 |
Spinal Cord
|
| 標識物 |
Unlabeled
|
| 参考文献 |
[Pub Med ID]1701448
|
| [注意事項] |
ご注文は10個から承ります
|
|
| メーカー |
品番 |
包装 |
|
RKL
|
GP-T065
|
1 EACH
|
※表示価格について
| 当社在庫 |
なし
|
| 納期目安 |
約10日
|
| 保存温度 |
-20℃
|
|



