|
※サムネイル画像をクリックすると拡大画像が表示されます。
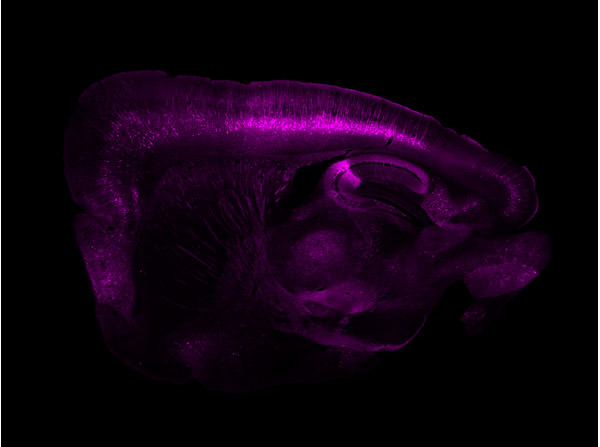
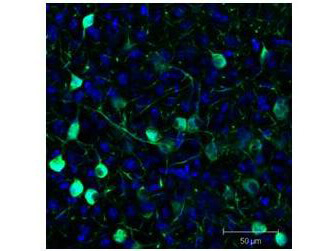
Immunofluorescence results using Goat Anti-GFP Antibody.Staining was performed on free-floating 40μm mouse brain sections. Heat antigen retrieval was performed for 30 minutes at 80°C in sodium citrate buffer (pH 8.9). Sections were blocked in 5% donkey serum with 0.25% Triton X-100 for 1h at RT, then incubated overnight at 4°C in a 1:1000 dilution of Goat Anti-GFP (p/n 600-101-215). Sections were then washed and incubated for 2h at RT in a 4μg/mL solution of donkey anti-rabbit AF647-conjugated secondary antibody. 10X fluorescence images were obtained using a Zeiss Axioscan automated slide scanning microscope. Low mag. Image courtesy of Michael Castle lab, University of California, San Diego.
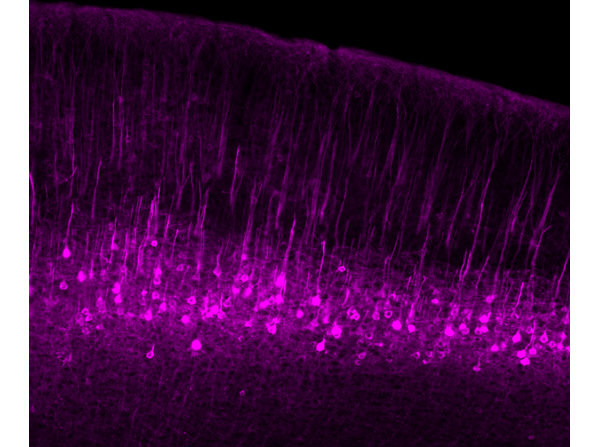
Immunofluorescence results using Goat Anti-GFP Antibody.Staining was performed on free-floating 40μm mouse brain sections. Heat antigen retrieval was performed for 30 minutes at 80°C in sodium citrate buffer (pH 8.9). Sections were blocked in 5% donkey serum with 0.25% Triton X-100 for 1h at RT, then incubated overnight at 4°C in a 1:1000 dilution of Goat Anti-GFP (p/n 600-101-215). Sections were then washed and incubated for 2h at RT in a 4μg/mL solution of donkey anti-rabbit AF647-conjugated secondary antibody. 10X fluorescence images were obtained using a Zeiss Axioscan automated slide scanning microscope. High mag. Image courtesy of Michael Castle lab, University of California, San Diego.
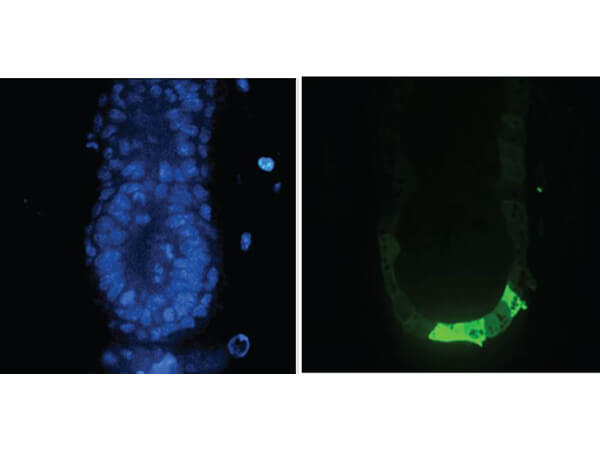
Immunofluorescence Microscopy of Anti-GFP (GOAT) Antibody. Tissue: E5.5 Hex-GFP transgenic mouse embryo. Primary antibody: Goat anti-GFP was used at 1:500 dilution. Secondary antibody: Fluorchrome conjugated Anti-goat IgG secondary antibody at 1:10,000 for 45 min at RT. Staining: GFP as green fluorescent signal with DAPI blue counterstain.
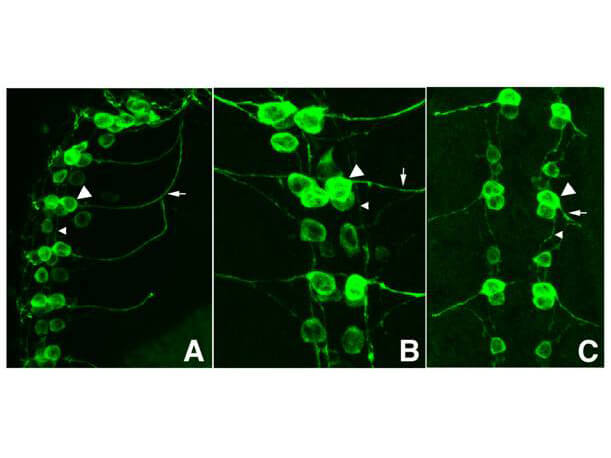
Immunofluorescence Microscopy of GFP-GOAT Antibody. Tissue: Drosophila melanogaster late stage embryonic central nervous system. Fixation: 0.5% PFA. Antigen retrieval: not required.Primary antibody: Anti-GFP antibody at a 1:1,000 for 1 h at RT.Secondary antibody: AlexaFluor 488? conjugated Anti-Goat antibody at 1:300 for 45 min at RT.Panel A: shows a lateral view (ventral left). Panels B and C: shows ventral views of whole mount embryos at 63x magnification (plus 2x digital zoom). In all panels, anterior is up.Staining: tau-GFP cell bodies (large arrowhead) and axons of motorneurons (arrow) and interneurons (small arrowhead) as green fluorescent signal.
Immunofluorescence Microscopy of Goat Anti-GFP Antibody. Tissue: Sf-1:Cre mice crossed to the Z/EG reporter line. Mouse brain (coronal view, 20X magnification). Fixation: 4%PFA/PBS with o/n fixation, and subsequently transferred to a 30% sucrose solution. Antigen retrieval: frozen in OCT freezing medium (Sakura) and cryostat sectioned at 40 microns. Primary antibody: Goat anti-GFP was used at 1:500 dilution in free floating immunohistochemistry to detect GFP. Secondary antibody: Fluorochrome conjugated Anti-goat IgG secondary antibody was used for detection at 1:500 at 1:10,000 for 45 min at RT. Localization: Sf-1+ neurons and their processes of the ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus. Staining: eGFP as green fluorescent signal and sections were counterstained with DAPI.
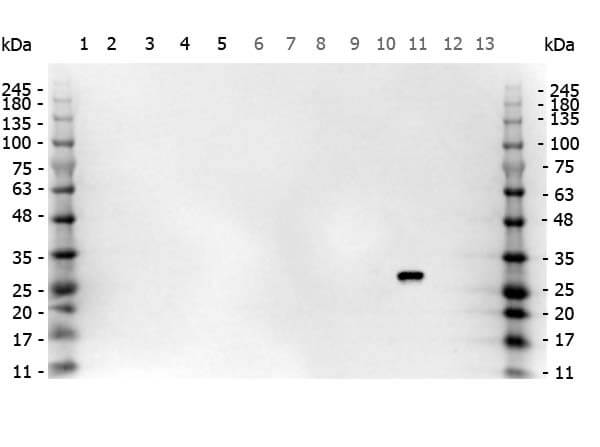
Multi-lysate Western Blot of Goat anti-GFP antibody. Marker: Opal Pre-stained ladder (p/n MB-210-0500). Lane 1: HEK293 lysate (p/n W09-000-365). Lane 2: HeLa Lysate (p/n W09-000-364). Lane 3: CHO/K1 Lysate (p/n W07-000-357). Lane 4: MDA-MB-231 (p/n W09-001-GK6). Lane 5: A431 Lysate (p/n W09-000-361). Lane 6: Jurkat Lysate (p/n W09-001-370). Lane 7: NIH/3T3 Lysate (p/n W10-000-358). Lane 8: E-coli HCP Control (p/n 000-001-J08). Lane 9: FLAG Positive Control Lysate (p/n W00-001-383). Lane 10: Red Fluorescent Protein (p/n 000-001-379). Lane 11: Green Fluorescent Protein (p/n 000-001-215). Lane 12: Glutathione-S-Transferase Protein (p/n 000-001-200). Lane 13: Maltose Binding Protein (p/n 000-001-385). Load: 10 μg of lysate or 50ng of purified protein per lane. Primary antibody: GFP antibody at 1ug/mL overnight at 4C. Secondary antibody: Peroxidase goat secondary antibody at 1:30,000 for 60 min at RT. Blocking Buffer: 1% Casein-TTBS (p/n MB-082) for 30 min at RT. Predicted/Observed size: 30 kDa for GFP.
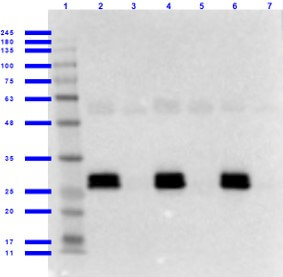
Western Blot of Goat anti-GFP Antibody with Serums. Lane 1: Opal Prestained Molecular Weight Marker (p/n MB-210-0500). Lane 2: GFP/Human Serum (p/n 000-001-215/D314-05) [0.01/0.02μL] [+]. Lane 3: Human Serum (p/n D314-05) [0.02μL] [-]. Lane 4: GFP/Mouse Serum (p/n 000-001-215/D308-05) [0.01/0.02μL] [+]. Lane 5: Mouse Serum (p/n D308-05) [0.02μL] [-]. Lane 6: GFP/Rat Serum (p/n 000-001-215/D310-05) [0.01/0.02μL] [+]. Lane 7: Rat Serum (p/n D310-05) [0.02μL] [-]. Primary antibody: Anti-GFP antibody at 1.0ug/mL overnight at 2-8°C. Secondary antibody: Donkey Anti-Goat IgG HRP secondary antibody (p/n CUSTmx8) at 1:40,000 for 30 min at RT. Blocking Buffer: BlockOut Buffer (p/n MB-073) for 1hr at RT. Predicted/Observed size: ~27kDa for GFP.
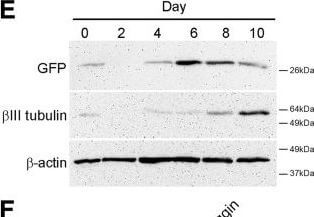
Npas4 expression during neural differentiation of ESCs. (A) RT-PCR analysis was used to determine the temporal expression profile of Npas4 mRNA in relation to various marker genes during N2B27 differentiation of mESCs (n?=?3). Primers to the reference gene β-actin were used as a loading control. The negative control reaction (−) contained water in place of template cDNA. (B) The changes in Npas4 expression during N2B27 differentiation were quantified using qRT-PCR. At each time point Npas4 expression was normalized to β-actin expression and fold changes are relative to Day 0 (undifferentiated mESCs). Mean values and standard deviations of three independent experiments (n?=?3) are displayed. (C)In situ hybridization analysis of Npas4 mRNA expression at Day 4 of N2B27 differentiation of mESCs. Representative images of differentiating colonies from two independent experiments (n?=?2) are shown. Top panel - Npas4 antisense probe; Bottom panel - Npas4 sense probe. Scale bar?=?100?μm. (D) Immunoblotting was used to determine the temporal expression profile of the Npas4 protein during N2B27 differentiation of mESCs. An antibody to the reference protein β-actin was used as a loading control (n?=?3). (E) Immunoblotting was used to determine the temporal expression profile of Sox1 in the 46C cell line (using an antibody to GFP) and βIII tubulin during N2B27 differentiation of mESCs. An antibody to the reference protein β-actin was used as a loading control (n?=?3). (F) RT-PCR analysis of NPAS4 mRNA in relation to various marker genes during Noggin-induced neural differentiation of hESCs (n?=?3). Primers to the reference gene β-ACTIN were used as a loading control. The negative control reaction (−) contained water in place of template cDNA. hESCs, human embryonic stem cells; mESCs, mouse embryonic stem cells; NS, neurospheres. Figure provided by CiteAb. Source: Stem Cell Res Ther, PMID: 24887558.
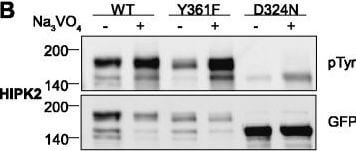
Tyrosine phosphorylation of HIPK mutants. HeLa cells were transiently transfected with the indicated expression constructs for HIPK1 (A), HIPK2 (B), HIPK3 (C) or HIPK4 (D). Sodium orthovanadate (Na3VO4) was added to every second sample for 1 h before lysis. GFP fusion proteins were immunoprecipitated and analysed by immunodetection with antibodies for pTyr and GFP. The panels are representative of 2?3 independent experiments. Figure provided by CiteAb. Source: Cell Commun Signal, PMID: 25630557.
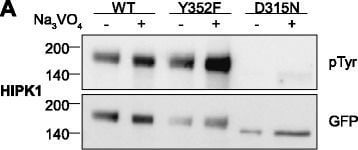
Tyrosine phosphorylation of HIPK mutants. HeLa cells were transiently transfected with the indicated expression constructs for HIPK1 (A), HIPK2 (B), HIPK3 (C) or HIPK4 (D). Sodium orthovanadate (Na3VO4) was added to every second sample for 1 h before lysis. GFP fusion proteins were immunoprecipitated and analysed by immunodetection with antibodies for pTyr and GFP. The panels are representative of 2?3 independent experiments. Figure provided by CiteAb. Source: Cell Commun Signal, PMID: 25630557.
|

|
|
Immunofluorescence results using Goat Anti-GFP Antibody.Staining was performed on free-floating 40μm mouse brain sections. Heat antigen retrieval was performed for 30 minutes at 80°C in sodium citrate buffer (pH 8.9). Sections were blocked in 5% donkey serum with 0.25% Triton X-100 for 1h at RT, then incubated overnight at 4°C in a 1:1000 dilution of Goat Anti-GFP (p/n 600-101-215). Sections were then washed and incubated for 2h at RT in a 4μg/mL solution of donkey anti-rabbit AF647-conjugated secondary antibody. 10X fluorescence images were obtained using a Zeiss Axioscan automated slide scanning microscope. Low mag. Image courtesy of Michael Castle lab, University of California, San Diego.
|
|
| 別品名 |
goat anti-GFP antibody, GFP, Green Fluorescent Protein, GFP antibody, Green Fluorescent Protein antibody, EGFP, enhanced Green Fluorescent Protein, Aequorea victoria, Jellyfish
|
| 適用 |
Western Blot
Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Immuno Fluorescence
|
| 免疫動物 |
Goat
|
| 標識物 |
Unlabeled
|
| 精製度 |
Affinity Purified
|
| Accession No.(Gene/Protein) |
P42212
|
| Tag情報 |
GFP
|
| 参考文献 |
[Pub Med ID]24887558
|
| [注意事項] |
濃度はロットによって異なる可能性があります。メーカーDS及びCoAからご確認ください。
|
|
| メーカー |
品番 |
包装 |
|
RKL
|
600-101-215S
|
25 UL
|
※表示価格について
| 当社在庫 |
なし
|
| 納期目安 |
約10日
|
| 保存温度 |
-20℃
|
|
※当社では商品情報の適切な管理に努めておりますが、表示される法規制情報は最新でない可能性があります。
また法規制情報の表示が無いものは、必ずしも法規制に非該当であることを示すものではありません。
商品のお届け前に最新の製品法規制情報をお求めの際はこちらへお問い合わせください。
|
※当社取り扱いの試薬・機器製品および受託サービス・創薬支援サービス(納品物、解析データ等)は、研究用としてのみ販売しております。
人や動物の医療用・臨床診断用・食品用としては、使用しないように、十分ご注意ください。
法規制欄に体外診断用医薬品と記載のものは除きます。
|
|
※リンク先での文献等のダウンロードに際しましては、掲載元の規約遵守をお願いします。
|
|
※CAS Registry Numbers have not been verified by CAS and may be inaccurate.
|










