|
※サムネイル画像をクリックすると拡大画像が表示されます。
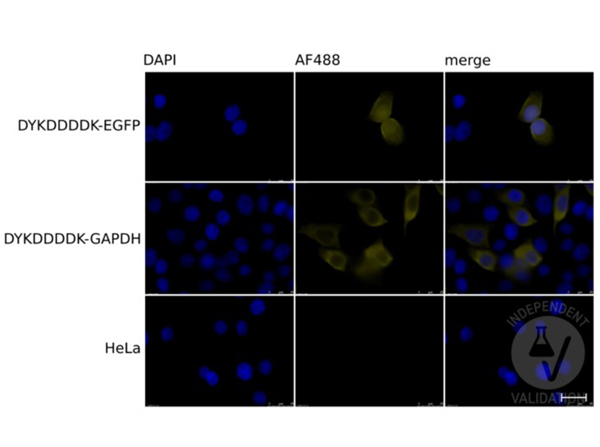
Immunofluorescence of the antibody for the detection of FLAGR conjugated proteins. Cells: HeLa cells transiently expressing DYKDDDDK-tagged EGFP (top row), or GAPDH (middle row), or mock-transfected HeLa cells (bottom row). Fixation: 4% PFA for 20-30 min at RT. Primary Antibody: DYKDDDDK Tag antibody diluted 1:200 overnight at 4°C. Secondary Antibody: chicken anti-rabbit AF488 antibody. Counterstain: DAPI for 10min at RT. Staining: DAPI (left column), DYKDDDDK Tag/AF488 (middle column), Merged DAPI and tag staining (right column). Independently Validated by?antibodies-online GmbH (p/n ABIN1043869/ ABIN99294) courtesy of?University of Bern.
Affinity Purified Antibody to detect FLAG conjugated proteins detects both C terminal linked and N terminal linked FLAG tagged recombinant proteins by western blot. This antibody was used at a dilution of 1:1,000 to detect 0.1 μg of recombinant protein containing either the FLAG epitope tag linked at the carboxy (C), Lane 2, or the amino (N), Lane 1, terminus of the recombinant protein. A 4-20% gradient gel was used to resolve the protein by SDS-PAGE. The protein was transferred to nitrocellulose using standard methods. After blocking, the membrane was probed with the primary antibody overnight at 4°C followed by washes and reaction with a 1:40,000 dilution of HRP conjugated Gt-a-Rabbit IgG (H&L) MX10 (code 611-103-122) for 30 min at room temperature. Bio-Rad's VersaDocR 4000 MP Imaging System was used to process the image. Other detection systems will yield similar results
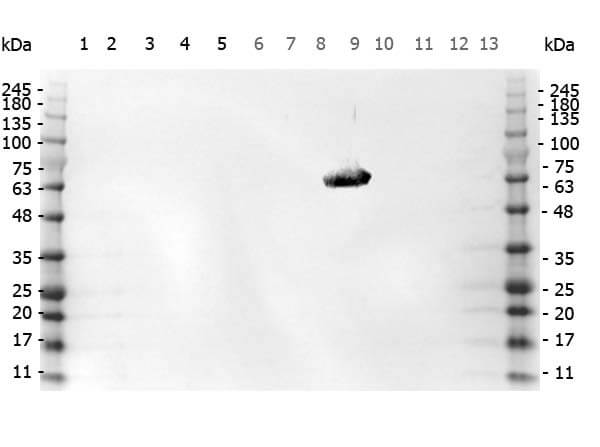
Western Blot of Rabbit anti-FLAG antibody. Marker: Opal Pre-stained ladder (p/n MB-210-0500). Lane 1: HEK293 lysate (p/n W09-000-365). Lane 2: HeLa Lysate (p/n W09-000-364). Lane 3: CHO/K1 Lysate (p/n W07-000-357). Lane 4: MDA-MB-231 (p/n W09-001-GK6). Lane 5: A431 Lysate (p/n W09-000-361). Lane 6: Jurkat Lysate (p/n W09-001-370). Lane 7: NIH/3T3 Lysate (p/n W10-000-358). Lane 8: E-coli HCP Control (p/n 000-001-J08). Lane 9: FLAG Positive Control Lysate (p/n W00-001-383). Lane 10: Red Fluorescent Protein (p/n 000-001-379). Lane 11: Green Fluorescent Protein (p/n 000-001-215). Lane 12: Glutathione-S-Transferase Protein. Lane 13: Maltose Binding Protein (p/n 000-001-385). Load: 10 μg of lysate or 50ng of purified protein per lane. Primary antibody: FLAG antibody at 1ug/mL overnight at 4C. Secondary antibody: Peroxidase rabbit secondary antibody (p/n 611-103-122) at 1:30,000 for 60 min at RT. Blocking Buffer: 1% Casein-TTBS for 30 min at RT. Predicted/Observed size: 55 kDa for FLAG.

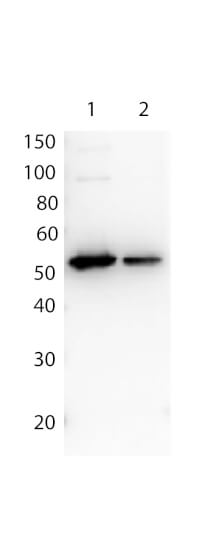
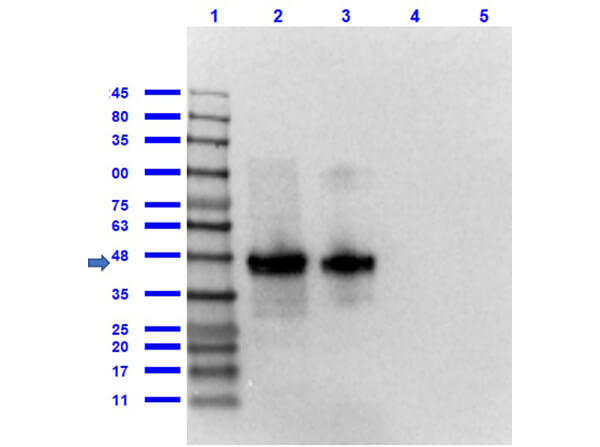
Western Blot of Rabbit anti-FLAG antibody. Lane 1: Opal Prestained Molecular Weight Marker (p/n MB-210-0500). Lane 2: FLAG Positive Control Lysate (p/n W00-E01-383) (10μg) [+]. Lane 3: 12 Epitope GST Tagged Lysate (p/n MB-302-0100) (10μg) [+]. Lane 4: rGST protein (p/n 000-001-200) (0.1μg) [-]. Lane 5: MBP protein (p/n 000-001-385) (0.1μg) [-]. Primary Antibody: Anti-FLAG at 1.0 μg/mL overnight at 2-8°C. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG Peroxidase (p/n 611-103-122) at 1:70,000 at RT for 30 mins. Block: BlockOut Buffer (p/n MB-073). Predicted MW: ~55kDa. Observed MW: ~48kDa. Exposure: 2 sec.
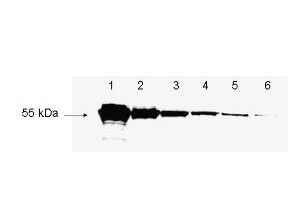
Rockland's antibody to detect FLAG? conjugated proteins is shown to detect as little as 3 ng of amino-terminal FLAG? tagged recombinant protein by western blot. This antibody was used at a 1:1,000 dilution to detect 3-fold serial dilutions of amino-terminal FLAG?-Bacterial Alkaline Phosphatase (BAP) fusion protein (Sigma P-7582) starting at 1.0 μg of protein as shown in lanes 1-6 respectively. A 4-20% gradient gel was used to separate the protein by SDS-PAGE. The protein was transferred to nitrocellulose using standard methods. After blocking, the membrane was probed with the primary antibody for 1 h at room temperature followed by washes and reaction with a 1:10,000 dilution of IRDyeR 800 conjugated Gt-a-Rabbit IgG (H&L) (code 611-132-122) for 30 min at room temperature. LICOR's OdysseyR Infrared Imaging System was used to scan and process the image. Other detection systems will yield similar results
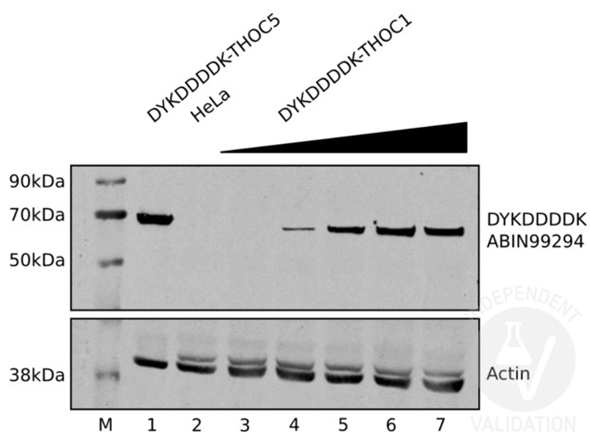
Western Blot of the antibody for the detection of FLAGR conjugated proteins. Negative Control: (Lane 2) Untransfected HeLa cell extracts. Positive Control: Transiently expressed DYKDDDDK-tagged THOC5 (lane 1). Positive Control: Increasing amounts of lysates from HeLa cells transiently expressing DYKDDDDK-tagged THOC1 (lanes 3 to 7). Primary Antibody: rabbit anti-DYKDDDDK Tag antibody or rabbit anti-actin antibody at 1:2000 for 1h at RT. Secondary Antibody: IRDye 800CW Goat anti-Rabbit at 1:10000 for 1h at RT. Independently Validated by?antibodies-online GmbH (p/n ABIN1043869/ ABIN99294) courtesy of?University of Bern.
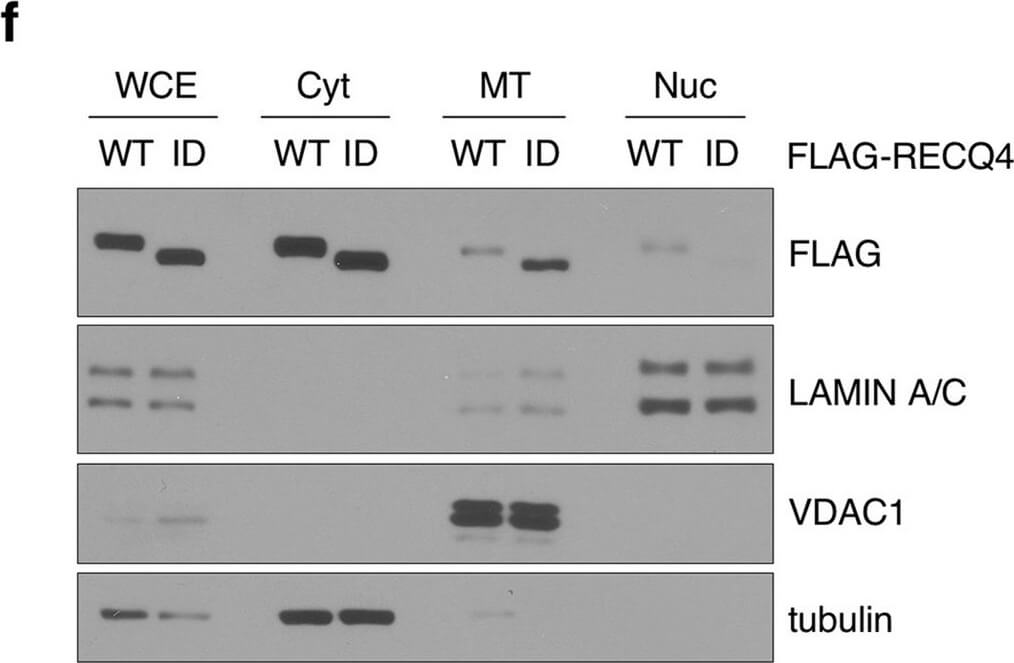
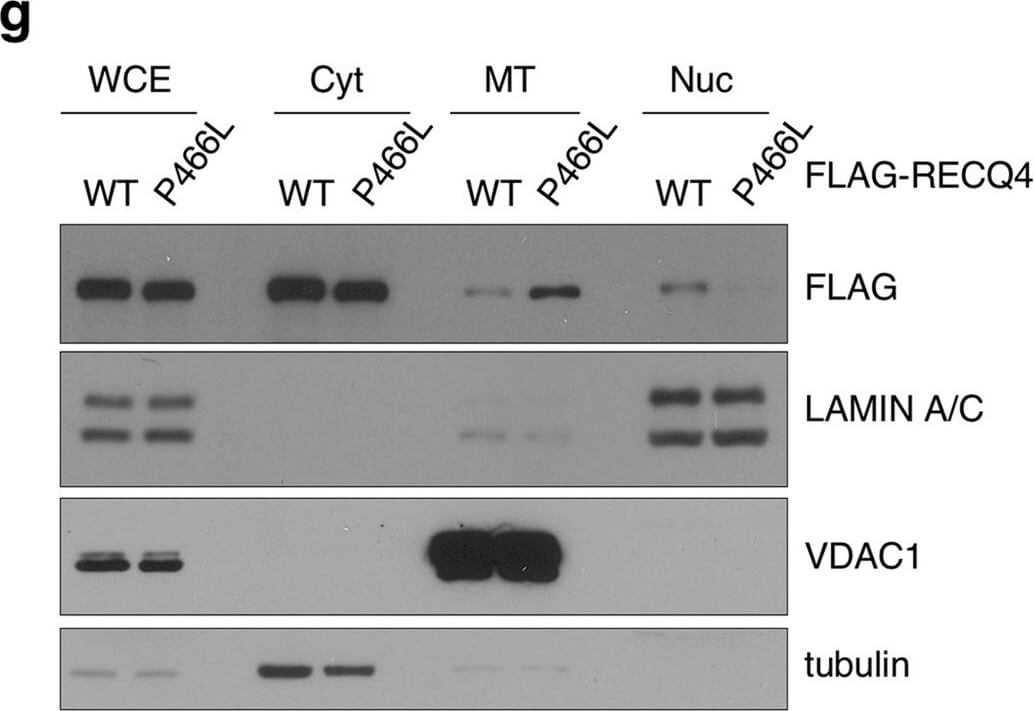
The P466L clinical mutation leads to RECQ4 mitochondrial accumulation. (a) Schematic of human RECQ4 WT, ID and P466L mutant proteins, including the SLD2 (green) and conserved SF2 helicase domains (yellow). (b) Western blot analysis of RECQ4 in WCEs and chromatin-bound (CB) fractions prepared from HEK293 WT or RECQ4 knockdown (KD) HEK293 cells generated by CRISPR technology. Tubulin is used as a loading control. (c) The effects of stable RECQ4 KD shown in (b) and complementation using FLAG-RECQ4 on cell growth as measured by crystal violet cell proliferation assays. Each value represents mean?±?standard deviation of 3 independent biological experiments, each with 3 triplicate reactions. (d) Western blot analysis for the presence of WT and mutant FLAG-RECQ4, p32, TWINKLE and TFAM in WCE (left) and immunoprecipitated (IP) with FLAG-RECQ4 complexes (right) in WCEs prepared from stable RECQ4 KD HEK293 cells expressing FLAG-RECQ4 WT, ID or P466L mutant. (e) gDNA levels relative to mtDNA in WCE (left) and MT (right) prepared from stable RECQ4 KD HEK293 cells expressing FLAG-RECQ4 WT, ID or P466L mutant. (f) Western blot analysis of stable RECQ4 KD HEK293 cells expressing FLAG-RECQ4 WT or ID mutant in WCEs and Cyt, MT, and fractions. Tubulin, VDAC1, and lamin A/C are loading and fractionation controls for Cyt, MT, and Nuc fractions, respectively. (g) Western blot analysis of RECQ4 in WCEs and Cyt, MT, and Nuc fractions prepared from stable RECQ4 KD HEK293 cells expressing FLAG-RECQ4 WT or P466L mutant. (h) Representative images showing immunofluorescent staining of FLAG-RECQ4 (green) in stable RECQ4 KD HEK293 cells expressing indicated WT and mutant FLAG-RECQ4 proteins. Mitotracker (red) was used to detect mitochondria, and DAPI (blue) was used to detect nuclei. Figure provided by CiteAb. Source: Sci Rep, PMID: 33046774.
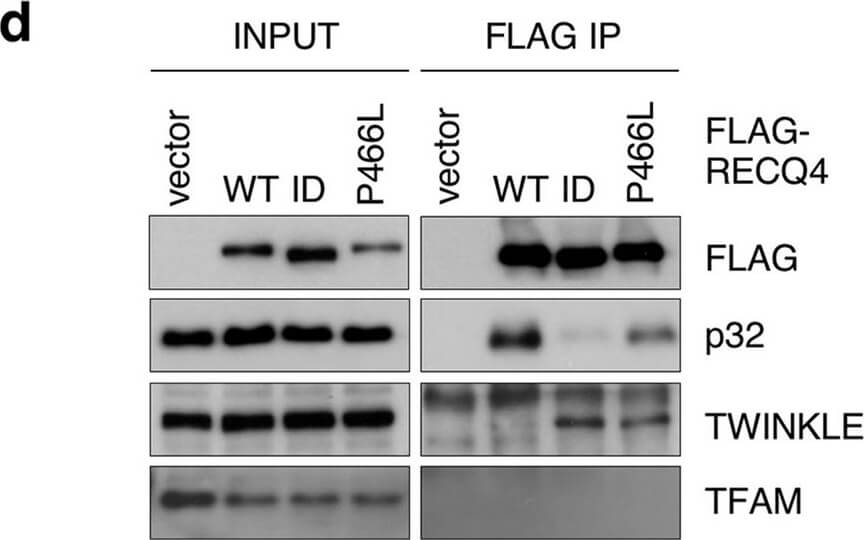
The P466L clinical mutation leads to RECQ4 mitochondrial accumulation. (a) Schematic of human RECQ4 WT, ID and P466L mutant proteins, including the SLD2 (green) and conserved SF2 helicase domains (yellow). (b) Western blot analysis of RECQ4 in WCEs and chromatin-bound (CB) fractions prepared from HEK293 WT or RECQ4 knockdown (KD) HEK293 cells generated by CRISPR technology. Tubulin is used as a loading control. (c) The effects of stable RECQ4 KD shown in (b) and complementation using FLAG-RECQ4 on cell growth as measured by crystal violet cell proliferation assays. Each value represents mean?±?standard deviation of 3 independent biological experiments, each with 3 triplicate reactions. (d) Western blot analysis for the presence of WT and mutant FLAG-RECQ4, p32, TWINKLE and TFAM in WCE (left) and immunoprecipitated (IP) with FLAG-RECQ4 complexes (right) in WCEs prepared from stable RECQ4 KD HEK293 cells expressing FLAG-RECQ4 WT, ID or P466L mutant. (e) gDNA levels relative to mtDNA in WCE (left) and MT (right) prepared from stable RECQ4 KD HEK293 cells expressing FLAG-RECQ4 WT, ID or P466L mutant. (f) Western blot analysis of stable RECQ4 KD HEK293 cells expressing FLAG-RECQ4 WT or ID mutant in WCEs and Cyt, MT, and fractions. Tubulin, VDAC1, and lamin A/C are loading and fractionation controls for Cyt, MT, and Nuc fractions, respectively. (g) Western blot analysis of RECQ4 in WCEs and Cyt, MT, and Nuc fractions prepared from stable RECQ4 KD HEK293 cells expressing FLAG-RECQ4 WT or P466L mutant. (h) Representative images showing immunofluorescent staining of FLAG-RECQ4 (green) in stable RECQ4 KD HEK293 cells expressing indicated WT and mutant FLAG-RECQ4 proteins. Mitotracker (red) was used to detect mitochondria, and DAPI (blue) was used to detect nuclei. Figure provided by CiteAb. Source: Sci Rep, PMID: 33046774.
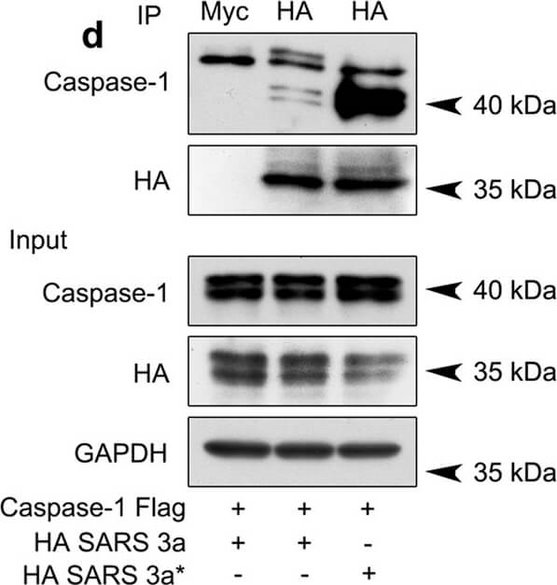
SARS 3a induces NLRP3 inflammasome activation by multiple mechanisms. A) Immunoblot analysis of the pro- and cleaved forms of caspase-1 and IL-1β after reconstitution of inflammasome in HEK 293T cells transfected with SARS 3a with or without NEK7 shRNA. B) Immunoblot analysis of the pro- and cleaved forms of caspase-1 and IL-1β after reconstitution of inflammasome and transfection with SARS 3a or SARS 3a C133A. C) Immunoblot analysis of the pro- and cleaved forms of caspase-1 and IL-1β after co-transfection with caspase-1, IL-1β, and SARS 3a or SARS 3a C133A. D) Immunoprecipitation analysis of interaction between SARS 3a or SARS 3a C133A and caspase-1. All western blot data are representative of two or three independent experiments Figure provided by CiteAb. Source: Cell Death Dis, PMID: 30185776.
The P466L clinical mutation leads to RECQ4 mitochondrial accumulation. (a) Schematic of human RECQ4 WT, ID and P466L mutant proteins, including the SLD2 (green) and conserved SF2 helicase domains (yellow). (b) Western blot analysis of RECQ4 in WCEs and chromatin-bound (CB) fractions prepared from HEK293 WT or RECQ4 knockdown (KD) HEK293 cells generated by CRISPR technology. Tubulin is used as a loading control. (c) The effects of stable RECQ4 KD shown in (b) and complementation using FLAG-RECQ4 on cell growth as measured by crystal violet cell proliferation assays. Each value represents mean?±?standard deviation of 3 independent biological experiments, each with 3 triplicate reactions. (d) Western blot analysis for the presence of WT and mutant FLAG-RECQ4, p32, TWINKLE and TFAM in WCE (left) and immunoprecipitated (IP) with FLAG-RECQ4 complexes (right) in WCEs prepared from stable RECQ4 KD HEK293 cells expressing FLAG-RECQ4 WT, ID or P466L mutant. (e) gDNA levels relative to mtDNA in WCE (left) and MT (right) prepared from stable RECQ4 KD HEK293 cells expressing FLAG-RECQ4 WT, ID or P466L mutant. (f) Western blot analysis of stable RECQ4 KD HEK293 cells expressing FLAG-RECQ4 WT or ID mutant in WCEs and Cyt, MT, and fractions. Tubulin, VDAC1, and lamin A/C are loading and fractionation controls for Cyt, MT, and Nuc fractions, respectively. (g) Western blot analysis of RECQ4 in WCEs and Cyt, MT, and Nuc fractions prepared from stable RECQ4 KD HEK293 cells expressing FLAG-RECQ4 WT or P466L mutant. (h) Representative images showing immunofluorescent staining of FLAG-RECQ4 (green) in stable RECQ4 KD HEK293 cells expressing indicated WT and mutant FLAG-RECQ4 proteins. Mitotracker (red) was used to detect mitochondria, and DAPI (blue) was used to detect nuclei. Figure provided by CiteAb. Source: Sci Rep, PMID: 33046774.
|

|
|
Immunofluorescence of the antibody for the detection of FLAGR conjugated proteins. Cells: HeLa cells transiently expressing DYKDDDDK-tagged EGFP (top row), or GAPDH (middle row), or mock-transfected HeLa cells (bottom row). Fixation: 4% PFA for 20-30 min at RT. Primary Antibody: DYKDDDDK Tag antibody diluted 1:200 overnight at 4°C. Secondary Antibody: chicken anti-rabbit AF488 antibody. Counterstain: DAPI for 10min at RT. Staining: DAPI (left column), DYKDDDDK Tag/AF488 (middle column), Merged DAPI and tag staining (right column). Independently Validated by?antibodies-online GmbH (p/n ABIN1043869/ ABIN99294) courtesy of?University of Bern.
|
|
| 別品名 |
rabbit antibody for the detection of FLAGTM conjugated proteins, rabbit anti DYKDDDDK
|
| 適用 |
Western Blot
Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay
|
| 免疫動物 |
Rabbit
|
| 標識物 |
Unlabeled
|
| 精製度 |
Affinity Purified
|
| Tag情報 |
FLAG
|
| 参考文献 |
[Pub Med ID]26635365
|
|
| メーカー |
品番 |
包装 |
|
RKL
|
600-401-383
|
250 UG
|
※表示価格について
| 当社在庫 |
なし
|
| 納期目安 |
約10日
|
| 保存温度 |
-20℃
|
|










