|
※サムネイル画像をクリックすると拡大画像が表示されます。
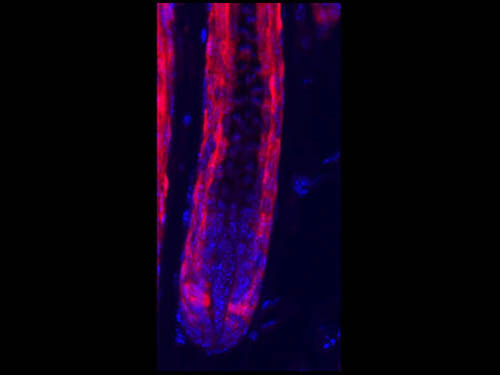
Immunofluorescence Microscopy of Rabbit Anti-RFP antibody. Tissue: HopERCre/+; R26Tom/+ mice. Fixation: 0.5% PFA. Antigen retrieval: Tamoxifen. Primary antibody: RFP antibody at 10 μg/mL for 1 h at RT. Secondary antibody: Fluorescein rabbit secondary antibody at 1:10,000 for 45 min at RT. Localization: RFP is nuclear and occasionally cytoplasmic. Staining: Hop-derived cells in the hair follicle, labeled in red. Courtesy of Rajan Jain at UPenn.
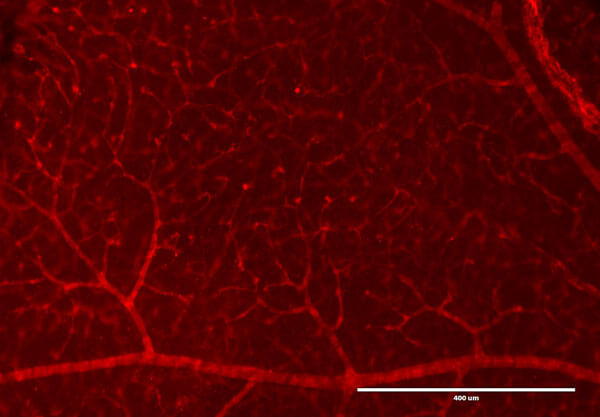
Immunofluorescence Microscopy of Rabbit Anti-RFP antibody. Tissue: DsRed transgenic mouse retina. Fixation: 4% PFA. Blocking: 3% BSA, 0.3% Triton Primary antibody: RFP antibody at 1:100 for 12 h at 4°C. Secondary antibody: Alexa488 secondary antibody at 1:10,000 for 4 hours at RT. Localization: RFP is nuclear and occasionally cytoplasmic. Staining: labeled in red. Courtesy of Ismail Zaitoun at Wisc.edu.
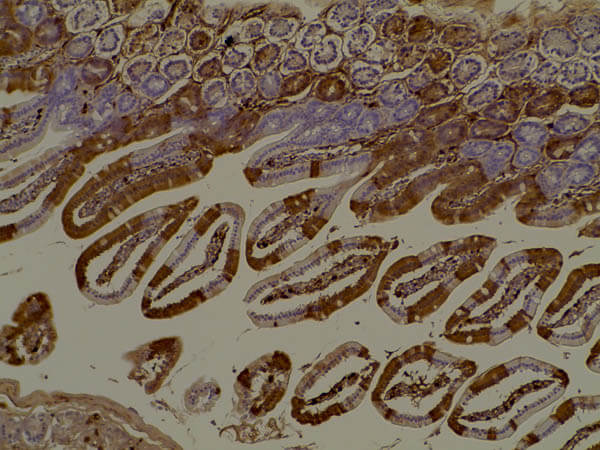
Immunohistochemistry of Anti-RFP Antibody. Tissue: Mouse gut tissue in tomato transgenic mice. Fixation: formalin fixed paraffin embedded. Antigen retrieval: heat 5 min at high temp in 1X rodent decloaker. Primary antibody: RFP antibody at 1:200 for 1 h 30 min at RT. Secondary Antibody: HRP anti-rabbit (p/n 611-103-122). Image courtesy: Kwan Hyun Kim.
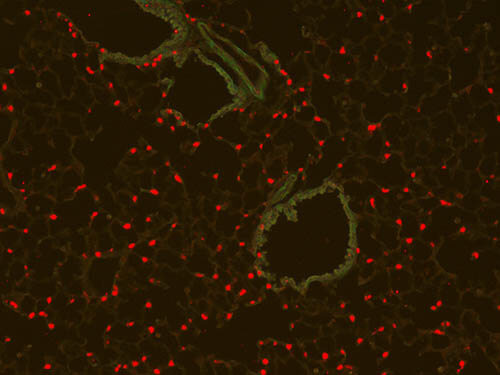
Immunofluorescence Microscopy of Rabbit Anti-RFP antibody. Tissue: (10X) Mouse lung tissue. Fixation: 4% PFA. Antigen retrieval: Heat. Primary antibody: Anti-RFP antibody at 1:50 for 1 h at RT. Secondary antibody: Fluorescein rabbit secondary antibody at 1:250 for 1 hr at RT. Staining: SPC+ cells are RFP positive in red. Courtesy of Johnathan C. Fox MD. PhD.
Immunofluorescence Microscopy of Rabbit Anti-RFP antibody. Tissue: (10X) Mouse E14.5 embryo heart tissue. Fixation: 4% PFA. Antigen retrieval: Heat. Primary antibody: Anti-RFP antibody at 1:50 for 1 h at RT. Secondary antibody: Fluorescein rabbit secondary antibody at 1:250 for 1 hr at RT. Staining: cardiac cells are RFP positive in red in tomato transgenic mice. Courtesy of Johnathan C. Fox MD. PhD.

Western Blot of RFP Antibody Pre-Absorbed. Lane 1: RFP (p/n 000-001-379). Lane 2: Human IgG (p/n 009-0102). Lane 3: Goat IgG (p/n 005-0102). Lane 4: Mouse IgG (p/n 010-0102). Load: 50ng per lane. Primary antibody: RFP Antibody Pre-Absorbed at 1:1,000 overnight at 4°C. Secondary antibody: Peroxidase conjugated rabbit secondary antibody (p/n 611-103-122) at 1:40,000 for 30 min at RT. Block: MB-070 Blocking Buffer for 30 min at RT. Predicted/Observed size: 27 kDa, 30 kDa.
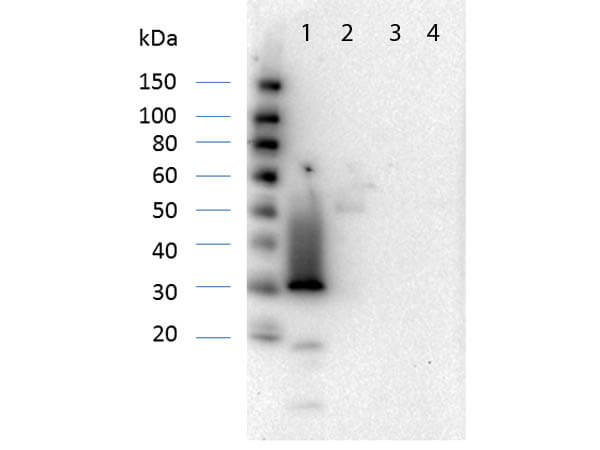
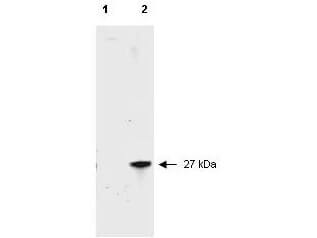
Western Blot of Rabbit anti-RFP Antibody. Lane 1: Opal Prestained Marker (p/n MB-210-0500). Lane 2: 50ng of RFP. Primary Antibody: Anti-RFP at 1μg/mL overnight at 2-8°C. Secondary Antibody: Goat anti-Rabbit HRP (p/n 611-103-122) at 1:70,000 for 30mins at RT. Block: BlockOut Universal blocking buffer (p/n MB-073). Expect ~27kDa.
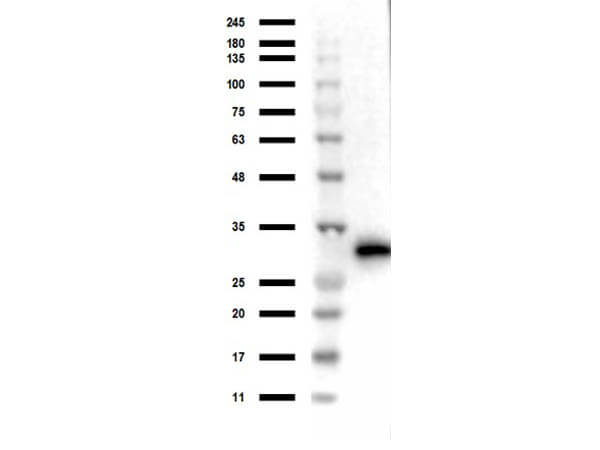
Western Blot of Rabbit anti-RFP antibody. Marker: Opal Pre-stained ladder (p/n MB-210-0500). Lane 1: HEK293 lysate (p/n W09-000-365). Lane 2: HeLa Lysate (p/n W09-000-364). Lane 3: CHO/K1 Lysate (p/n W07-000-357). Lane 4: MDA-MB-231 (p/n W09-001-GK6). Lane 5: A431 Lysate (p/n W09-000-361). Lane 6: Jurkat Lysate (p/n W09-001-370). Lane 7: NIH/3T3 Lysate (p/n W10-000-358). Lane 8: E-coli HCP Control (p/n 000-001-J08). Lane 9: FLAG Positive Control Lysate (p/n W00-001-383). Lane 10: Red Fluorescent Protein (p/n 000-001-379). Lane 11: Green Fluorescent Protein (p/n 000-001-215). Lane 12: Glutathione-S-Transferase Protein. Lane 13: Maltose Binding Protein (p/n 000-001-385). Load: 10 μg of lysate or 50ng of purified protein per lane. Primary antibody: RFP antibody at 1ug/mL overnight at 4C. Secondary antibody: Peroxidase rabbit secondary antibody (p/n 611-103-122) at 1:30,000 for 60 min at RT. Blocking Buffer: 1% Casein-TTBS for 30 min at RT. Predicted/Observed size: 30 kDa for RFP.
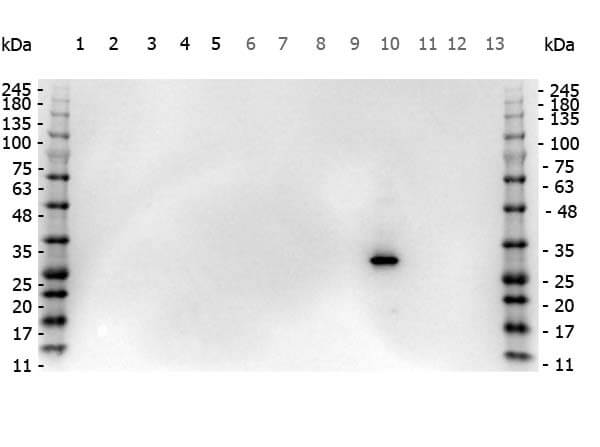
Western Blot of Rabbit Anti-RFP MW Hu, Ms, Rt Antibody. Lane 1: Opal Prestained Molecular Weight Marker (p/n MB-210-0500). Lane 2: RFP/HEK293T WCL (p/n 000-001-379/W09-001-GX5) [0.05/10μg] [+]. Lane 3: HEK293T Whole Cell Lysate [-]. Lane 4: RFP/NIH/3T3 Whole Cell Lysate (p/n 000-001-379/W10-000-358) [0.05/10μg] [+]. Lane 5: NIH/3T3 Whole Cell Lysate [-]. Lane 6: RFP/PC-12 Whole Cell Lysate (p/n 000-001-379/W12-001-GL9) [0.05/10μg] [+]. Lane 7: PC-12 Whole Cell Lysate [-]. Primary Antibody: Anti-RFP at 1:1000 overnight at 2-8°C. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG Peroxidase (p/n 611-103-122) at 1:70,000 at RT for 30 mins. Predicted/Observed MW: ~27kDa. Exposure: 2 sec.
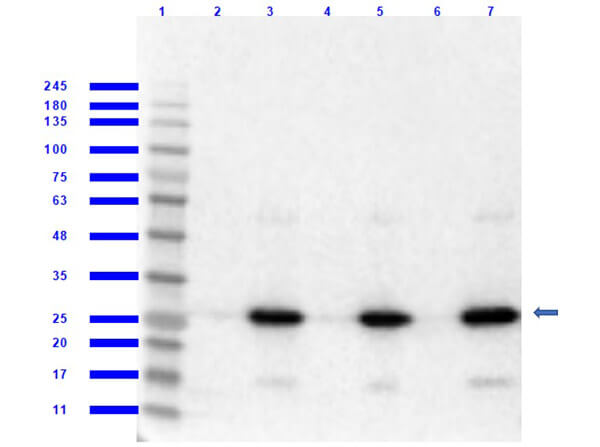
Western blot of RFP recombinant protein detected with Rockland's polyclonal anti-RFP antibody. Lane 1 shows no reaction against a GFP recombinant protein present in 10 μg of HeLa cell extract. Lane 2 shows a single band detected in 10 μg of a HeLa lysate containing RFP recombinant protein as a 27 kDa band. A 4-12% Bis-Tris gradient gel (Invitrogen) was used for SDS-PAGE. The membrane was blocked and then probed with Anti-RFP diluted 1:2,500 for 1 h at RT followed by washes and reaction with a 1:5,000 dilution of IRDye?800 conjugated Goat-a-Rabbit IgG [H&L] MX (611-132-122). IRDye?800 fluorescence image was captured using the OdysseyR Infrared Imaging System developed by LI-COR. IRDye is a trademark of LI-COR, Inc. Other detection systems will yield similar results.
|

|
|
Immunofluorescence Microscopy of Rabbit Anti-RFP antibody. Tissue: HopERCre/+; R26Tom/+ mice. Fixation: 0.5% PFA. Antigen retrieval: Tamoxifen. Primary antibody: RFP antibody at 10 μg/mL for 1 h at RT. Secondary antibody: Fluorescein rabbit secondary antibody at 1:10,000 for 45 min at RT. Localization: RFP is nuclear and occasionally cytoplasmic. Staining: Hop-derived cells in the hair follicle, labeled in red. Courtesy of Rajan Jain at UPenn.
|
|
| 別品名 |
rabbit anti-RFP antibody, DsRed, rDsRed, Discosoma sp. Red Fluorescent Protein, Red fluorescent protein drFP583.
|
| 非交差(吸収処理)種 |
Human
Mouse
Rat
|
| 適用 |
Western Blot
Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Immunohistochemistry
Immuno Fluorescence
|
| 免疫動物 |
Rabbit
|
| 標識物 |
Unlabeled
|
| 精製度 |
Affinity Purified
|
| Accession No.(Gene/Protein) |
Q9U6Y8
|
| Gene Symbol |
DsRed
|
| Tag情報 |
RFP
|
| 参考文献 |
[Pub Med ID]38338800
|
| [注意事項] |
濃度はロットによって異なる可能性があります。メーカーDS及びCoAからご確認ください。
|
|
| メーカー |
品番 |
包装 |
|
RKL
|
600-401-379
|
100 UG
|
※表示価格について
| 当社在庫 |
なし
|
| 入荷予定 |
あり
|
| 納期目安 |
発注済・入荷予定
|
| 保存温度 |
-20℃
|
|
※当社では商品情報の適切な管理に努めておりますが、表示される法規制情報は最新でない可能性があります。
また法規制情報の表示が無いものは、必ずしも法規制に非該当であることを示すものではありません。
商品のお届け前に最新の製品法規制情報をお求めの際はこちらへお問い合わせください。
|
※当社取り扱いの試薬・機器製品および受託サービス・創薬支援サービス(納品物、解析データ等)は、研究用としてのみ販売しております。
人や動物の医療用・臨床診断用・食品用としては、使用しないように、十分ご注意ください。
法規制欄に体外診断用医薬品と記載のものは除きます。
|
|
※リンク先での文献等のダウンロードに際しましては、掲載元の規約遵守をお願いします。
|
|
※CAS Registry Numbers have not been verified by CAS and may be inaccurate.
|










